As Nestlé continues its journey towards sustainable sourcing, the company has recently unveiled groundbreaking initiatives designed to significantly reduce cocoa supply emissions. Renowned globally in the food and beverage industry, Nestlé’s renewed commitment to environmental sustainability has garnered considerable attention.
Collaborating with key suppliers such as Cargill and Export Trading Group’s (ETG) Beyond Beans, Nestlé has launched transformative projects spanning five years. These initiatives mark a significant step forward in advancing agroforestry practices and promoting sustainable cocoa farming methods.
Nestlé’s ambitious efforts aim to revolutionize the cocoa industry by implementing innovative strategies for emission reductions. By embracing sustainable practices and fostering partnerships across the supply chain, Nestlé is demonstrating its leadership in driving positive change towards a more environmentally responsible cocoa sector.
Fostering Partnership with Cargill and ETG | Beyond Beans for Sustainable Projects
Nestlé’s partnership with its suppliers Cargill and ETG | Beyond Beans aligns with its objective to achieve net zero by 2050. They will primarily target carbon reduction and removal with Nestle’s cocoa supply chain.
The key objectives of the projects are:
Cocoa & Forest Initiative (CFI)
It envisions planting over 2 million shade trees, managed by 20,000 farmers in Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire. These projects are projected to cut down over 500,000 MTs of carbon dioxide over twenty years.
The shade trees mitigate exposure to sunlight and preserve moisture for the cocoa crops in dry seasons. They optimize water resources and boost biodiversity on farms. Most importantly, they are highly efficient in absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere.
Under CFI, Nestlé also plans to cut cocoa supply emissions by encouraging farmers to shift towards regenerative agriculture. The core focus would be to support reforestation in degraded cocoa farming lands.
To support this program, Darrell High, global cocoa manager at Nestlé has said:
“We’re working to address our emissions all the way to the farms we source from. Long-lasting forest protection can only happen when collaborating with fully committed suppliers, just like Cargill and ETG | Beyond Beans. We also depend on the participation of local communities, who have an impact on the forests and can help find land-use solutions that are best suited for the local reality.”
Involving Locals and Community Engagement Activities
Community engagement and social inclusions of the locals come under Nestlé’s Income Accelerator Program. It’s specifically designed to support cocoa-farming families. The projects would ensure that farmers receive their due rewards and incentives for the labor they put into planting and nurturing the cocoa crops.
Ursule Gatta, Cargill’s sustainability partnership officer in Côte d’IvoireOur said,
“Our ambition is to scale up the project to cover 18 cooperatives over five years, aligned with the Nestlé Income Accelerator program.”
Cargill and ETG | Beyond Bean projects strive to engage the local communities whose agricultural lands have not been cultivated for a long time. These two firms will take over those lands for reforestation and redevelopment purposes.
They aim to plant tree nurseries for cocoa seed cultivation. Apart from financial aid, the companies will offer technical assistance and consultations to the farmers to carry out sustainable agricultural practices.
Both the supplier chains play crucial roles in facilitating the implementation of Nestlé’s Income Accelerator Program within these projects.
Unlocking Global Reforestation Program (GRP) to Mitigate Cocoa Emissions by 2030
As mentioned on Nestlé’s official website, it has set an ambitious reforestation goal aka the Global Reforestation Program (GRP). The company pledges to grow 200 million trees by 2030 in and around farms where it sources its key ingredients.
Nestle’s primary focus will be on deforested land. They will also work to establish conservation and restoration as standard practices across their supply chains.
Why Nestlé’s GRP is crucial for climate change? Well, reforestation and restoration of degraded landscapes actively aid in long-term carbon removal and storage. These efforts are part of Natural Climate Solutions (NCS), essential for combating climate change.
Therefore, Nestlé with its land-use footprint must urgently invest in conservation and restoration to reach the 1.5°C target set by the International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in the COP21 Paris agreement.
The company’s Net Zero Roadmap incorporates carbon removals, primarily from sourcing ingredients. They believe that natural climate remedies in their supply chain can potentially eliminate GHGs from the atmosphere. This is expected to further boost their decarbonization goal of achieving 2.0 million tCO2e removals by 2030.
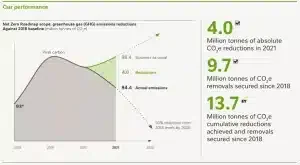
The chart examines Nestlé’s sustainability performance in 2021
source: www.nestle.com/sustainability
The main points highlighted in this chart are:
-
By 2025, reduce absolute emissions by 20%
from 2018 levels -
By 2030, reduce absolute emissions by 50% from 2018 levels
Simultaneously, it is also important to track the viability of the projects to enjoy long-term benefits. One such way is monitoring the number of trees planted and the volume of CO2 removed.
As per reports, Nestlé anticipates installing high-resolution satellite imaging technology to ensure the smooth running of its cocoa supply emission control strategy. With this tool, they can track the sustainability of the cultivated trees and evaluate the overall outcome of the reforestation projects.
One can foresee that Nestlé aims to revolutionize the cocoa industry’s approach to mitigating emissions with innovative strategies and partnerships. They are investing at the landscape level to achieve both environmental and socio-economic benefits.