In its recent webinar, the MSCI Carbon Markets provided a comprehensive review of the voluntary carbon market (VCM) in 2023, highlighting both notable advancements and notable challenges that characterized the year.
Throughout 2023, the voluntary carbon market experienced significant progress, marked by increasing interest and participation from various stakeholders including corporations, governments, and investors. This surge in engagement reflects a growing recognition of the importance of voluntary carbon offsetting as a tool for mitigating climate change and achieving carbon neutrality goals.
One of the key developments in 2023 was the emergence of innovative financing mechanisms and platforms that facilitated greater accessibility and transparency within the voluntary carbon market. These initiatives played a crucial role in democratizing access to carbon offset projects, enabling a broader range of organizations and individuals to participate in carbon offsetting efforts.
Additionally, 2023 saw a notable expansion in the scope and diversity of carbon offset projects, with a growing emphasis on nature-based solutions such as reforestation, afforestation, and sustainable agriculture. This trend reflects a shift towards more holistic approaches to carbon offsetting that prioritize both carbon sequestration and ecosystem conservation.
However, despite these positive developments, the voluntary carbon market also faced significant hurdles in 2023. One of the primary challenges was the lack of standardized methodologies and verification processes, which resulted in inconsistencies and discrepancies in carbon offset quality and credibility. Addressing these issues will be crucial for fostering trust and confidence among market participants and ensuring the integrity of voluntary carbon offset projects.
Moreover, the voluntary carbon market encountered criticism and scrutiny regarding issues of additionality, permanence, and double counting, raising concerns about the effectiveness and legitimacy of certain carbon offset projects. Overcoming these challenges will require greater collaboration and alignment among stakeholders to establish clear standards and best practices for carbon offsetting within the voluntary market.
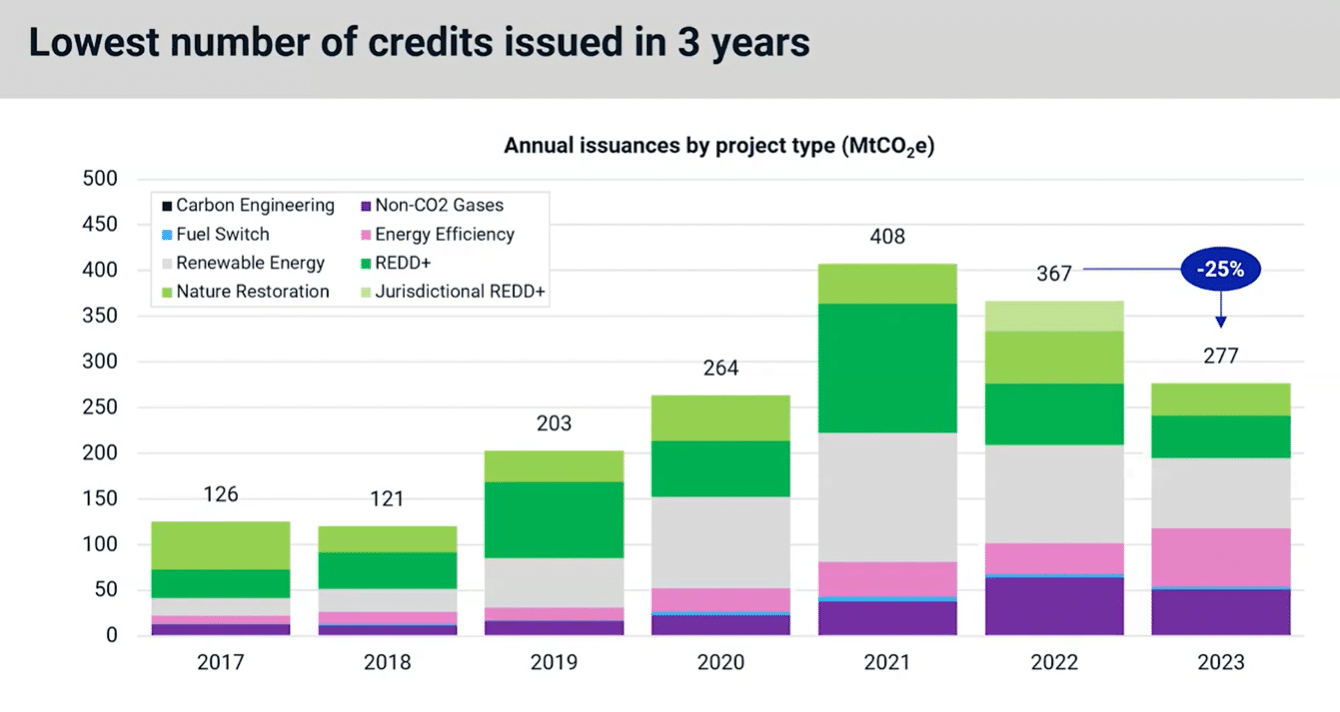
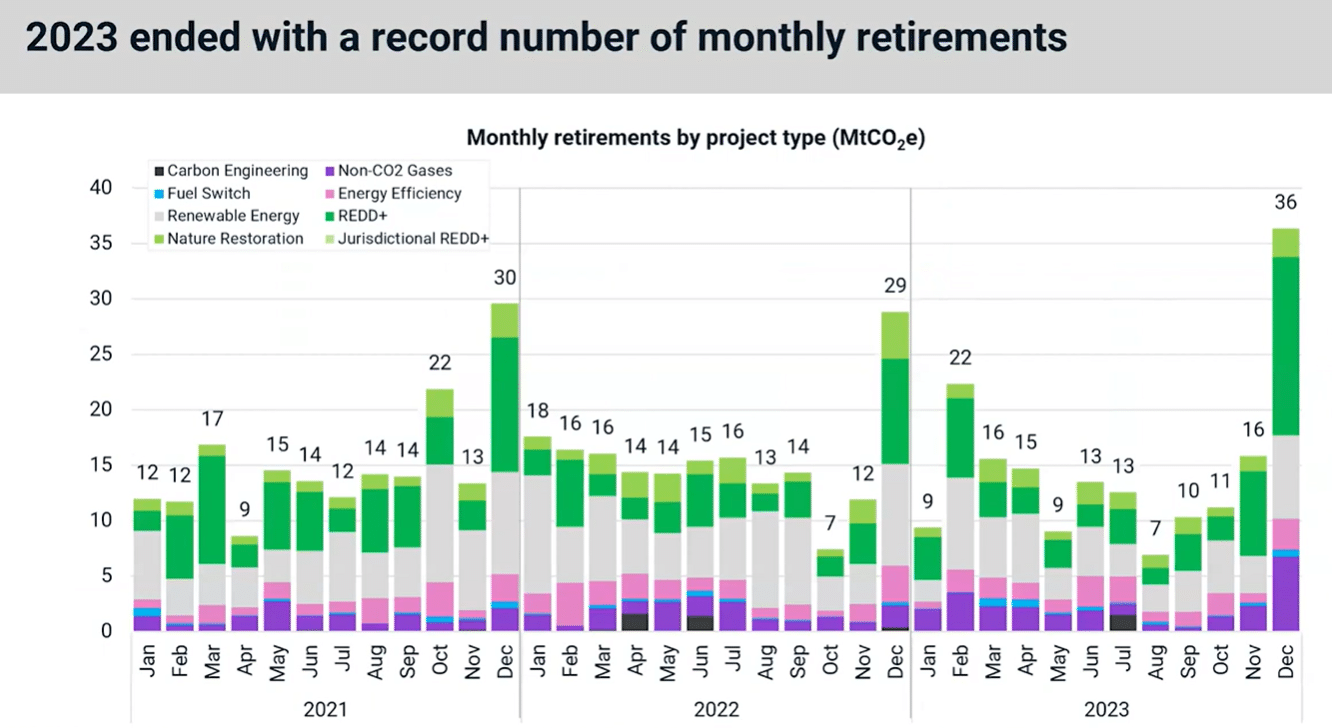
The review includes key developments from 2023 and the potential inflection points to watch out for in 2024. Notably, the findings show that 2023 has the lowest number of credits issued in 3 years. In contrast, the year ended with a record number of monthly retirements.
Here’s a recap of the webinar, focusing on carbon credit issuances and retirements, demand, key market players, investment, major policy developments, and 2024 outlook.
Peaks, Valleys, and 2023’s Record Retirements
In 2023, credit issuances recorded the lowest annual total in 3 years after falling 25% year-on-year, as seen below. This slow down in supply was largely due to Nature-based and renewable energy projects issuing their lowest annual amounts in 5 and 4 years, respectively.
The MSCI report saw retirements rallied in Q4 2023, the second highest quarter on record. And that’s despite the slow down in corporate activity in mid-year. This momentum seems to have been carried into January this year.
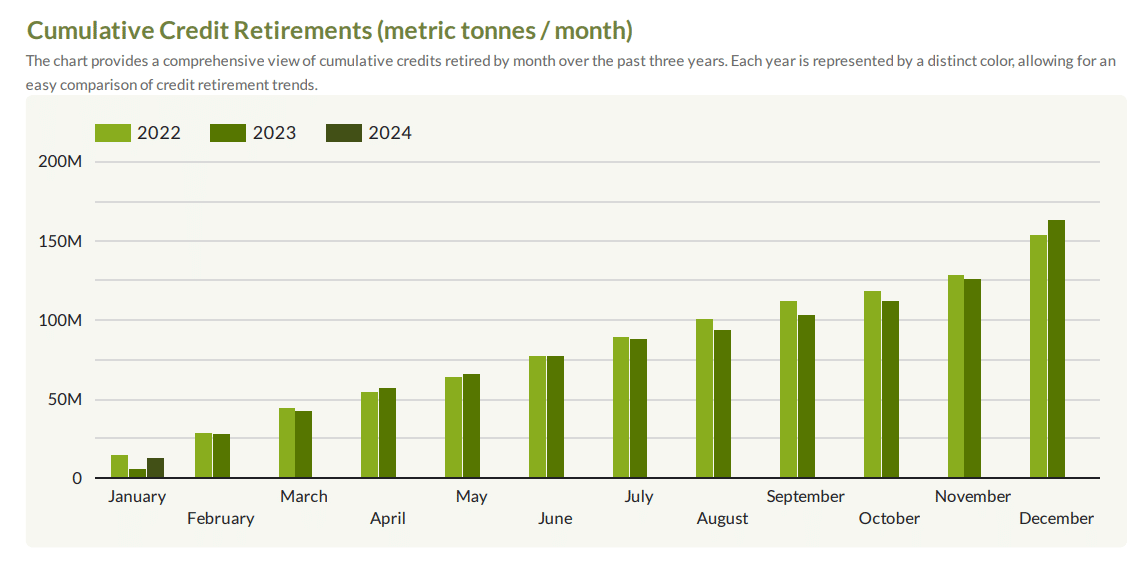
In fact, that’s the second highest January to date and may even exceed the 17 MtCO2 set in 2022. December 2023 alone has seen 36 megatons of credit retirement, setting a new monthly high, around 25% above the previous high record.
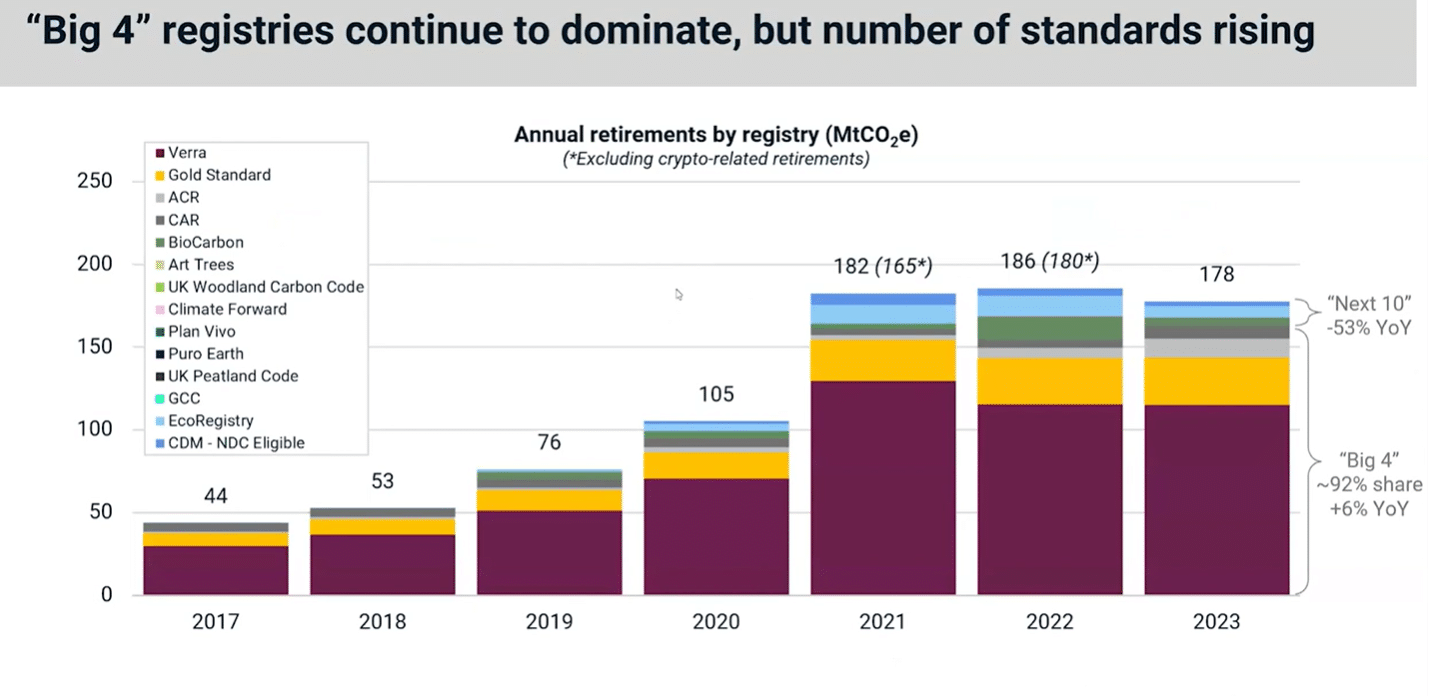
When it comes to registries, the four largest, namely Verra, Gold Standard, ACR, and CAR continue to dominate the market. They provide more than 90% of the credits retired last year.
Retirements from these “Big 4” registries actually rose last year by 6%, while retirements across the next ten prominent names dropped slightly in 2023.
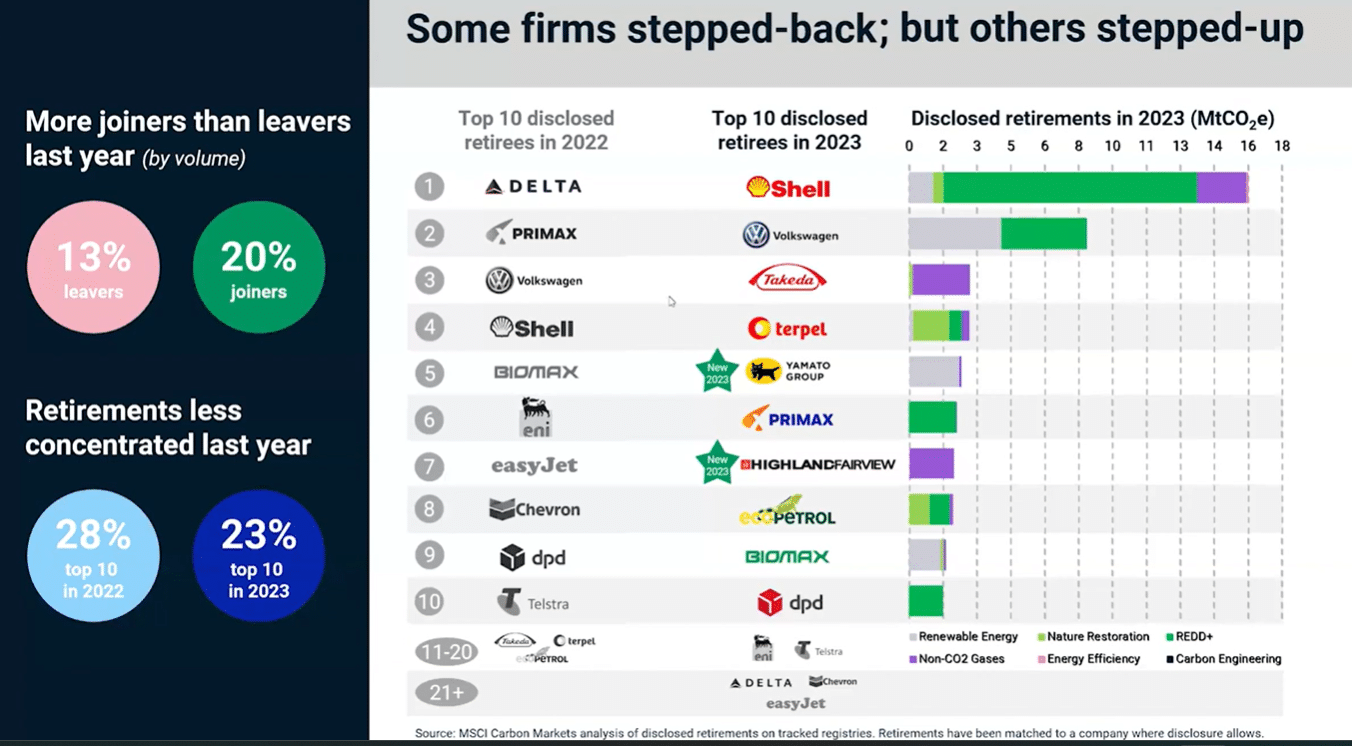
Of the top 10 retirees, Delta Airlines aced the first spot. They were also the largest retiree corporate in 2021 and 2022. While some of these companies exited the top 10 last year, others remain while new ones entered the market.
Shell topped the list in 2023 with around 16 million metric tonnes, followed by Volkswagen with over 8 MtCO2e. Overall, there are more joiners than leavers last year when it comes to retiring credits.
Unlocking the Nascent Carbon Removal Market
Gaining a lot of interest in 2023 is the nascent CDR market, referring to high permanent engineered carbon removals. These include biochar and direct air capture, which usually command a premium price than other project types. That’s because they’re known to be of higher quality and high durability.
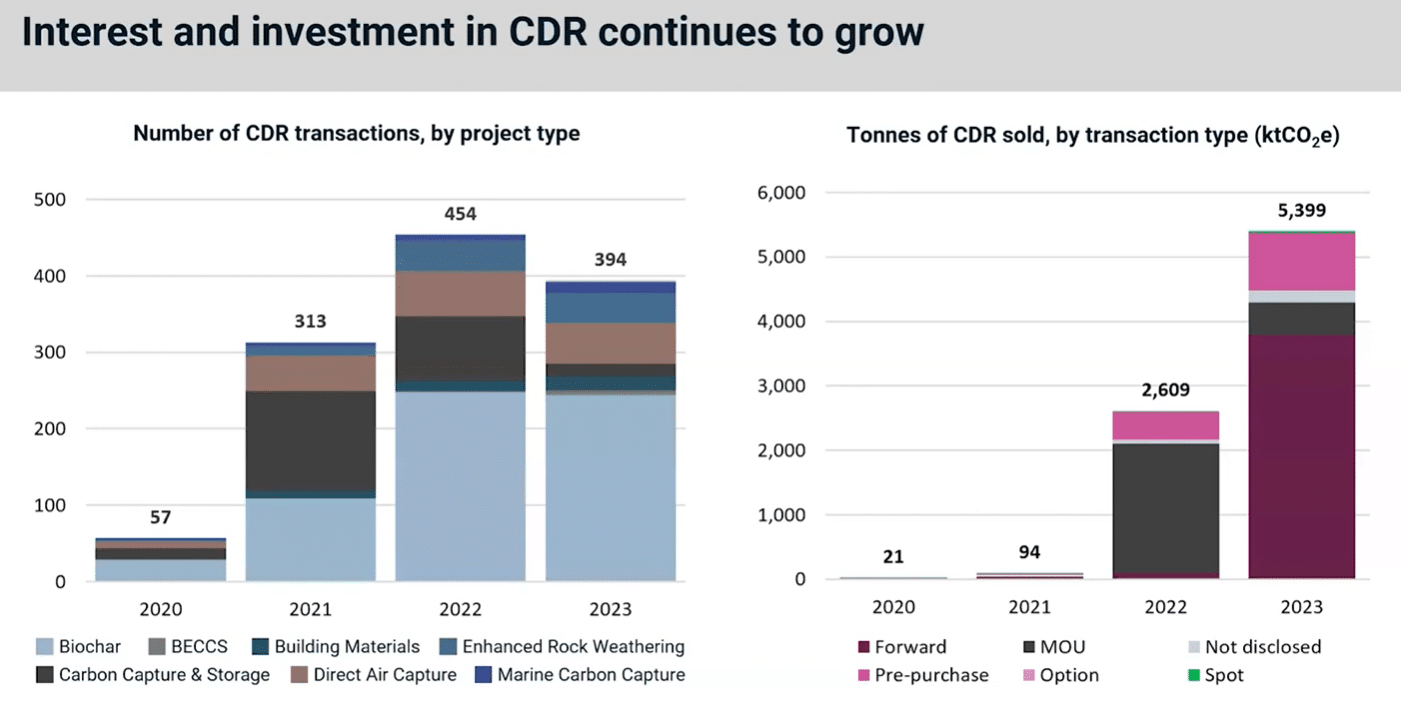
Last year, the number of CDR transactions fell slightly year-on-year. But the quantity of credits, represented by the right hand chart, increased significantly to 5.4 million.
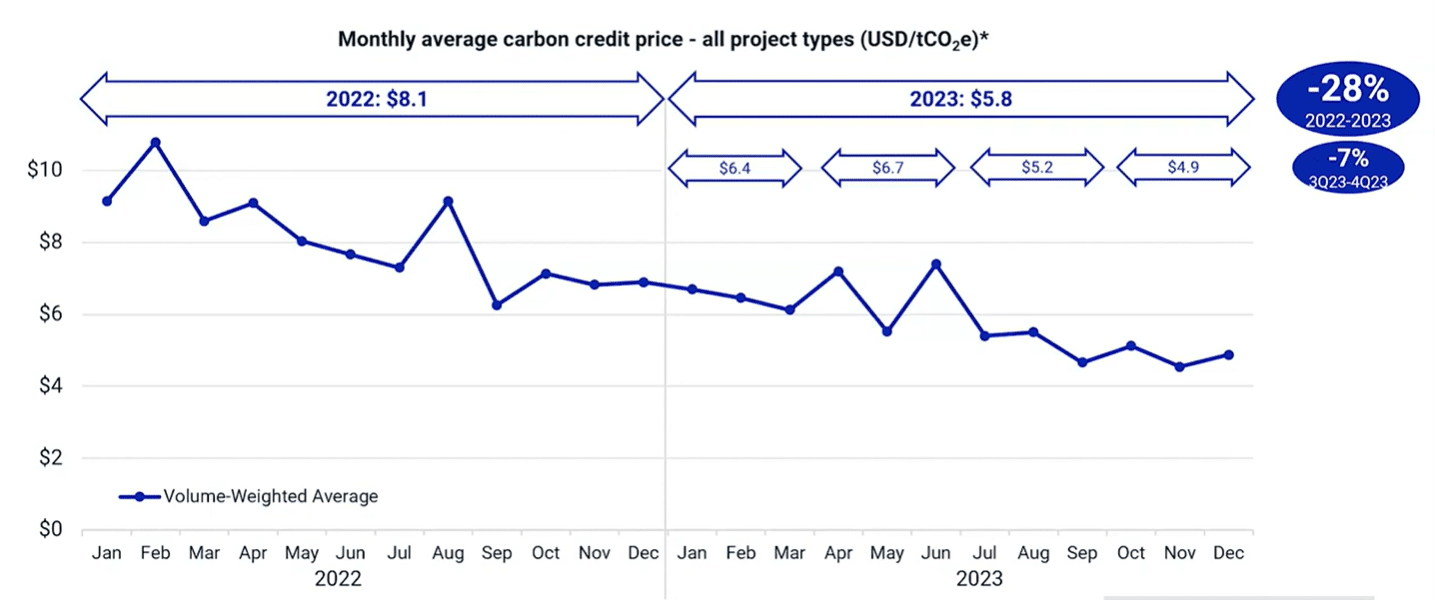
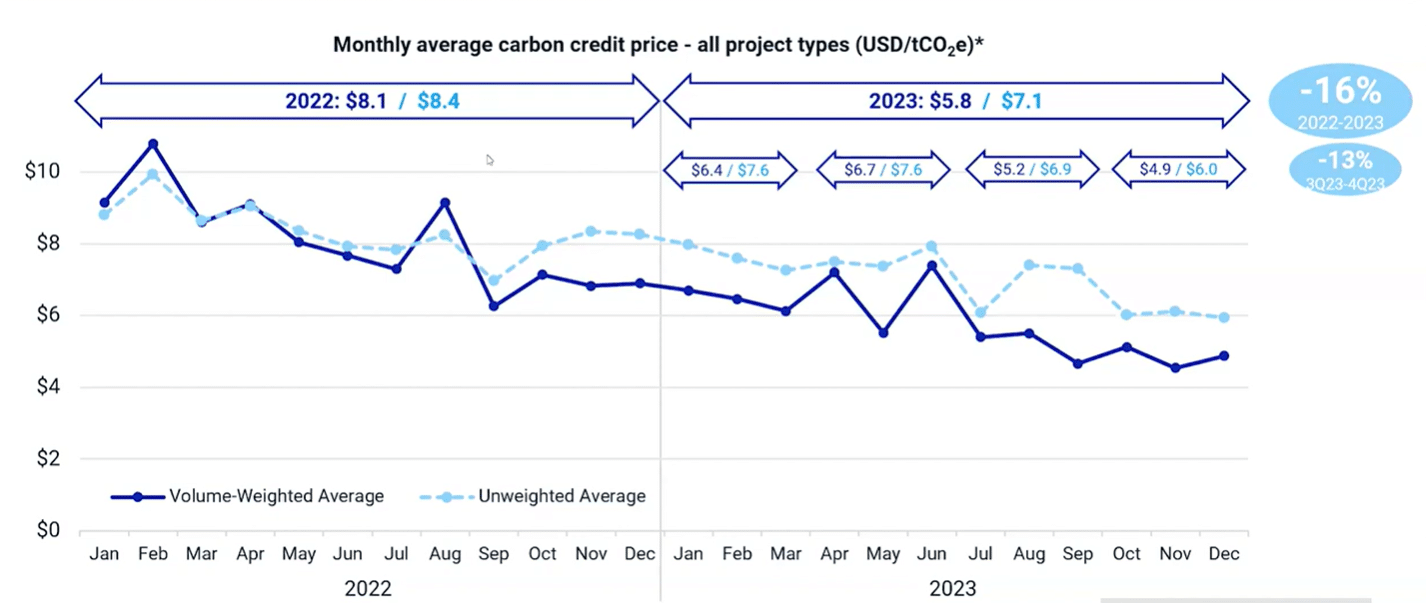
Navigating the Ups and Downs of Carbon Credit Prices
The declining trend in 2022 was carried over into the first half of 2023. But looking at the average level, the drop wasn’t that much. It was only 16% lower in 2022 compared to 2023.
In terms of price by project type for last year, all of them were lower in Q4, resulting in full year price declines. REDD+ projects saw the least drop, 15%, while renewable energy experienced the largest price decrease, 39%.
Both energy efficiency (pink line) and REDD+ (green line) projects were subject to increased media and academic scrutiny in 2023. They sustained weaker prices.
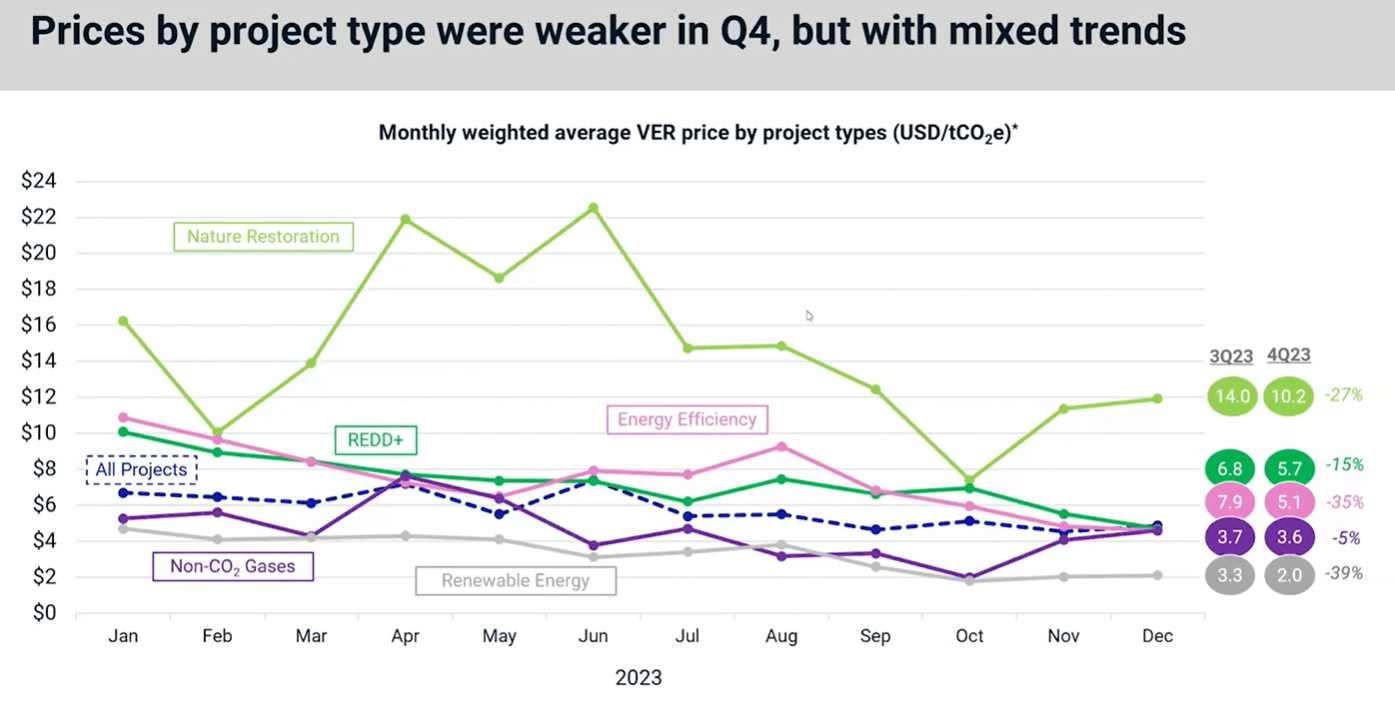
Interestingly, both nature restoration and non-CO2 gasses projects rebounded in November and December last year. Meanwhile, energy efficiency, REDD+, and non-CO2 gasses converged around the same price level at $4.65 by the end of the year.
This suggests that the market is not distinguishing between these project types, potentially signaling a weak market environment.
Policy Developments in 2023: From EU Directives to COP28’s Uncharted Territories
Last year also saw some major policy developments. For instance, the EU’s green claims directive aims to empower consumers for the green transition directive. It bans claims of neutral, reduced, or positive climate impact based on carbon offsetting, on the grounds that it’s a misleading consumer practice.
Moreover, the VCMI carbon integrity claims, the Claims Code of Practice (CCPs), is a significant regulation for the VCM.
There are also landmark regulations of market trading and standards wherein national governments are stepping in. For example, the US Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) introduced proposed guidance for trading of voluntary carbon credit derivative contracts.
In the Global South, there has been growth in national carbon credit markets while carbon pricing systems and schemes are being proposed in several African countries. Amid increased scrutiny in carbon credits certified by Verra, the leading carbon certifier updated its standards.
At the COP28 climate summit, carbon markets find their footing amid Article 6 frustrated talks. Article 6.2 rules are mostly in place but there’s a lack of Article 6.4 agreement on key steps. Disagreements centered on integrity concerns, yet Article 6 agreements are moving ahead.
Looking forward, MSCI Head of Carbon Markets, Guy Turner, raised a pertinent question: “Could we be at an inflection point for the market in 2024?”
There could be several inflection points, five in particular.
- The potential new sources of demand driven by CORSIA, VCMI, SBTi, and more compliance markets in near and long term.
- Quality initiatives moving into implementation.
- Jurisdictional approaches are starting to take off – whether by governments or donor institutions. High interests are observed in jurisdictional soil carbon and blue carbon.
- Increasing clarity for corporations on claims and disclosures on the use of credits, with the EU and UK taking the lead.
- Macroeconomic cycle turning but political uncertainties
In the ever-evolving landscape of the voluntary carbon market, 2023 marked both triumphs and challenges. From record retirements to the rise of CDR investments, the market navigated uncertainties. As 2024 unfolds, potential inflection points await, shaping the future trajectory of the global carbon market.